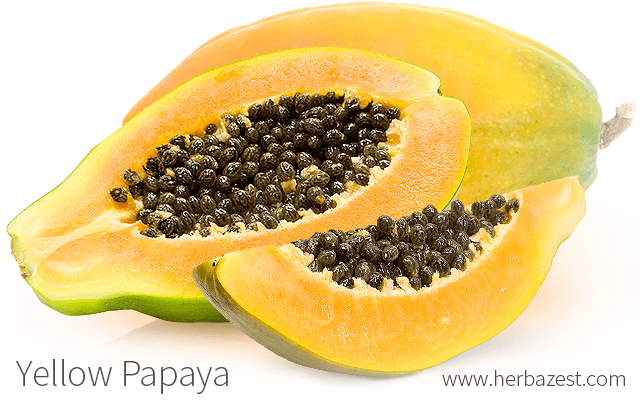
Yellow papayas are golden-fleshed cultivars of the Carica papaya plant. Highly prized in the international tropical fruit market, many commercially-abundant yellow papayas have been derived from the Hawaiian 'Solo' variety, with 'Waimanalo,' 'Kapoho,' 'Rainbow,' 'Coorg Honey Dew,' and 'Honey Gold' among the most popular cultivars. These papayas are jam-packed with essential nutrients, which support their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Yellow Papaya Benefits
Fetching high prices and greatly influencing market standards, the yellow-fleshed papayas of Hawaii are among the best in the world. Several important strains have been carefully inbred in controlled greenhouse environments for their premium fruit quality and improved resistance against plant viruses. 'Waimanalo' and 'Kapoho,' for example, are now considered to be genetically stable, with seeds producing true, uniform plant cultivars.
Yellow papayas hold powerful antioxidant properties that not only foster healthy wound healing, but also work to support cellular repair. They are thought to improve several major cardiovascular conditions, including atherosclerosis. Furthermore, the antimicrobial action of yellow papaya supports this immune-strengthening quality by helping the body to defend itself against bacterial and viral infections.
While papaya's papain is a digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins - thus being beneficial for treating gastrointestinal complains, such as constipation, diarrhea, and indigestion - the cosmetic industry has long valued yellow papayas for their skin-rejuvenating and healing properties. The high content of papain in the milky latex of the unripe fruit can help clear acne and improve complexion thanks to its exfoliating action on the skin. Furthermore, yellow papaya can also lower blood pressure, glucose, and harmful cholesterol levels.
Yellow Papaya Nutrition
Like its salmon-colored and deep red counterparts, the yellow papaya possesses a rich store of phytoconstituents known as carotenoids. These naturally-occurring plant pigments not only give yellow papaya its color, but are responsible for promoting vitamin A as well as for protecting the skin against ultraviolet sun damage. However, it should be noted that the yellow papaya contains no lycopene, but it is instead richer in other carotenoids, such as zeta carotene and cryptoxanthin.
THE AMOUNT OF VITAMIN A CONTAINED IN A YELLOW PAPAYA IS COMPARABLE TO THAT OF TOMATOES, PROVIDING UP TO 10% OF THE RECOMMENDED VALUE EACH DAY.
As a general rule, yellow papayas provide a bit less sugar than the red ones, but are said to have an intermediate glycemic index. However, their dietary fiber keeps the body feeling full longer, making it a helpful component of healthful weight management regimes.
Moreover, yellow-fleshed papaya nutrition includes impressive amounts of vitamin C; a single 100-g serving can provide up to 75% of the daily recommended intake. Other notable nutrients in yellow papaya include fats, carbs, potassium, and magnesium, which help to boost overall energy production.
The yellow papaya is a deliciously-wholesome fruit containing a wide array of nutrients. Inexpensive and available throughout many regions of the world, yellow papayas provide much of the same benefits of red papaya and other varieties and can be an excellent addition to any diet.
Sources
- Fruits of Warm Climates, Papaya, Carica papaya L.
- International Tropical Fruits Network, Papaya – Common varieties
- Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, Ascorbic acid, vitamin A, and mineral composition of banana (Musa sp.) and papaya (Carica papaya) cultivars grown in Hawaii, 2006
- National Library of Medicine, Lycopene
- U.S. Pacific Basin Agricultural Research Center, Vitamin and mineral content of tropical fruit cultivars grown in Hawaii
- University of Hawaii, Sunrise solo: A different colored solo papaya | Papaya production in Hawaii
- University of the West Indies at Mona - Jamaica, Papaya – pawpaw
- USDA Nutrient Database, Papayas, raw