Main Benefits of Pumpkin
Some of the following health benefits of pumpkin, recognized in ancient healing rituals, have been substantiated in recent years through modern scientific studies and plant research.
Treating Common Skin Conditions
Pumpkins are believed to have originated in North or Central America. In that region, traditional healers have long used pumpkin as a treatment for common skin conditions. In the Yucatan Peninsula, for example, pumpkins are applied topically to burns, sores, and blisters. The effectiveness of this practice has been validated by modern science.
Powerful antioxidants in pumpkin are beneficial for maintaining the health of the skin. Oil extracted from pumpkin seeds contains about 50% vitamin E, which shields the skin from damage caused by free radicals and is used for the necessary cellular communication the skin needs to heal itself. A one-ounce serving of pumpkin seeds can provide about 28% of the recommended intake of zinc, which also plays a role in wound healing.
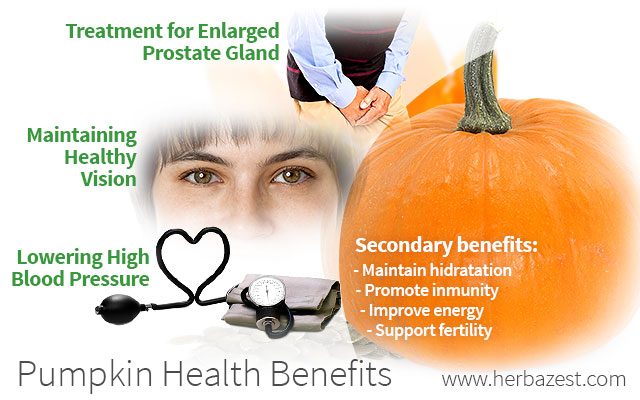
Treatment for Enlarged Prostate Gland
Traditional folk medicine touts pumpkin seeds as an effective treatment for prostate enlargement. Anti-inflammatory agents, known as phytosterols, combine with the healing properties of zinc to potentially reduce the size of the prostate.
Maintaining Healthy Vision
Pumpkins get their distinctive color from the presence of plant carotenes, which are easily converted into vitamin A in the body. Both vitamin A and beta-carotene help to protect the eyes from damage, especially when adjusting to the dark after being in bright light.
Lowering High Blood Pressure
Among the various other important nutritional benefits of pumpkin is its well-documented hypotensive effect. Pumpkins contain an abundance of phytosterols and vitamin E, which protect the heart by widening the blood vessels, preventing blood clots, and lowering blood pressure.
Secondary Nutritional Benefits of Pumpkin
The many essential nutrients found in pumpkin help keep the body in working order. These nutritional benefits include:
Maintaining proper hydration. Staying hydrated is of profound importance for the human body, which uses water to maintain healthy cellular growth and to perform just about every other major bodily function. Therefore, pumpkins - which are low in calories and composed of about 90% water - have been used as a cure for thirst and dehydration.
Promoting immune health. Vitamin E and zinc work together to help activate different cells in the immune system, which makes pumpkin beneficial for preventing common illnesses.
Improving energy levels. Pumpkins can provide a necessary energy boost as a treatment for general fatigue. A one-ounce serving of pumpkin seeds provides about 53% of the recommended daily intake of magnesium, a vital nutrient that is required for the production of energy.
Supporting reproductive health. Vitamin A and zinc play an important role in supporting healthy fetal growth and development during pregnancy while caring for the reproductive system overall. In some ancient traditions, pumpkins were used as a fertility boost and as a treatment to help new mothers produce milk for nursing.
A delicious crop that has been consumed by humans for thousands of years, pumpkin is a healthy herb with lots of nutritional benefits, such as antioxidant, antidiabetic, and anti-anemic properties.
The rise in popularity of certain serious illness has increased the need for knowledge about pumpkin. Therefore, the scientific community has performed research on the health benefits pumpkin provides, which may help to unlock the mystery of the plant's hidden potential, especially in terms of its use as a safe, inexpensive, and highly-effective alternative to popular medicine.
Sources
- European Food Research & Technology, Variability of vitamin E content in pumpkin seeds (Cucurbita pepo L), 1996
- International Journal of Food Science and Technology, Vitamins composition of pulp, seed and rind of fresh and dry Rambutan Nephelium Lappaceum and squash Cucurbita pepo L., 2013
- National Institutes of Health, Magnesium | Vitamin A | Vitamin C | Vitamin E
- Nutrition Research Reviews, Medicinal and biological potential of pumpkin: an updated review, 2010
- USDA Nutrient Database
- Journal of Medicinal Food, Antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects of pumpkin seed oil, 2012 | The role of carotenoids in human health, 2002
- Power Foods, pp. 25, 57, 358, 371
- Rosemary Gladstar's Herbal Recipes for Vibrant Health, pp. 239, 241, 253, 358