In the past, red clover could only be found growing wild across much of Europe and Asia. Like many herbs, it has also been used over the years as a medicinal agent against skin conditions and respiratory complications. Even as recently as the last century, red clover has been keenly sought after for its status as a "blood purifier." Modern times, however, have seen a particular upward spike in its use against hormonal imbalances - mostly menopause symptoms - due to its phytoestrogenic activity.
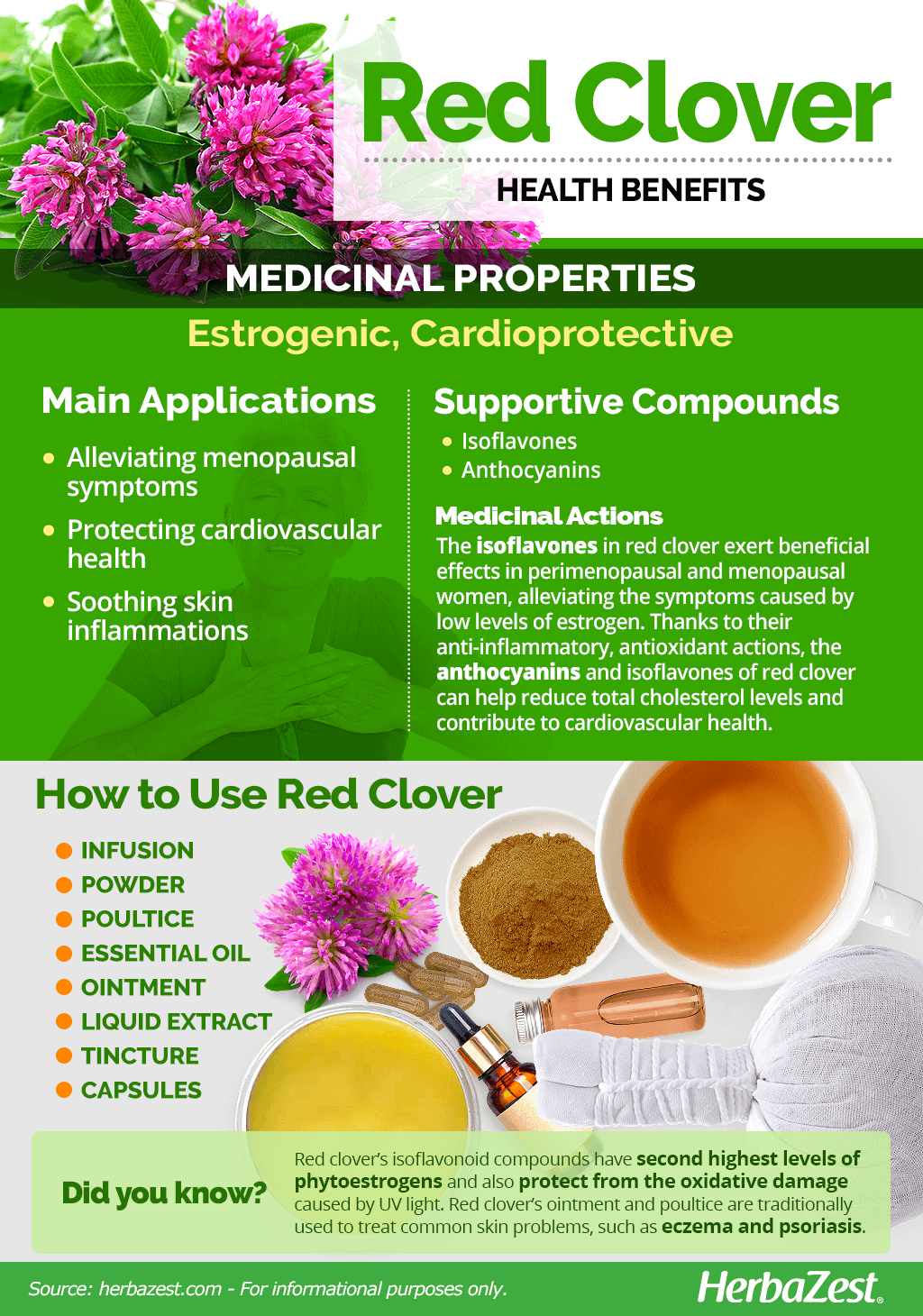
Red Clover Medicinal Properties
Health Benefits of Red Clover
Historically, the medicinal properties of red clover have been used to treat a wide variety of health conditions, such as asthma, whooping cough, and gout. Modern science has corroborated some of these traditional uses and revealed new applications for this medicinal herb. These are some of the most remarkable red clover's benefits:
Alleviating menopause symptoms. The phytoestrogenic properties of red clover are effective for the treatment of female hormonal imbalances.
Protecting cardiovascular health. Red clover is rich in flavonoids, which not only keep cholesterol levels in check, but also reduce the risk of heart disease.
Soothing skin inflammations. The anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of red clover are popularly used to treat common skin problems, such as eczema, psoriasis, and sunburns.
Red clover is also popularly used for treating respiratory issues and fighting osteoporosis.
How It Works
As recently as the 20th century, red clover was known as a "blood purifier."
Red clover contains volatile oils (benzyl alcohol and methyl salicylate), coumarins, and cyanogenic glycosides. However, the compounds responsible for red clover's newfound popularity are isoflavones, which occur in high levels in this herb. Isoflavones are phytoestrogenic compounds, which have similar effects as estrogen in humans.1
Isoflavones bind themselves to estrogen receptors found on certain cells throughout the body. Once attached, their presence in the cells mimic the effects of estrogen. These reactions are not quite the same as true estrogen's would be, but they are still more beneficial than if nothing was bound to the receptors at all.
Anthocyanins are pigments with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. The combined action of anthocyanins and isoflavones are a powerful aid in the treatment of common skin problems, such as eczema and psoriasis as well as for protecting against the harmful effects of UV light on the skin and reducing sunburn inflammation.2,3
Red clover extract has been shown to improve hair and skin health as well as boost libido, mood, sleep, and energy in postmenopausal women.3
Recent studies have also shown evidence that red clover extract can scale down the levels of total cholesterol in menopausal women, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.4
Other herbs with estrogenic properties are aguaje, dong quai, ginseng and soybean, whereas maca, despite not having phytoestrogens, naturally stimulates the endocrine system, relieving the symptoms of hormonal imbalance. On the other hand, avocado, olives (particularly olive oil), lucuma, and quinoa also help regulate cholesterol levels and promote cardiovascular health.
Red Clover Side Effects
Red clover is considered generally safe and does not have any dangerous side effects for the majority of the population, although it can occasionally cause skin rashes, nausea, and headaches.
Red Clover Cautions
Red clover contraindications are important as women who are pregnant, have a past history of breast cancer, or have blood clotting disorders should not take red clover products.
It should be noted that consuming phytoestrogenic supplements for a long time can hinder the ability of the body to produce its own estrogen supply.
- Medicinal action Cardioprotective, Estrogenic
- Key constituents Isoflavones, anthocyanins
- Ways to use Capsules, Hot infusions/tisanes, Liquid extracts, Tincture, Poultice, Powder, Ointment, Essential oil
- Medicinal rating (3) Reasonably useful plant
- Safety ranking Use with caution
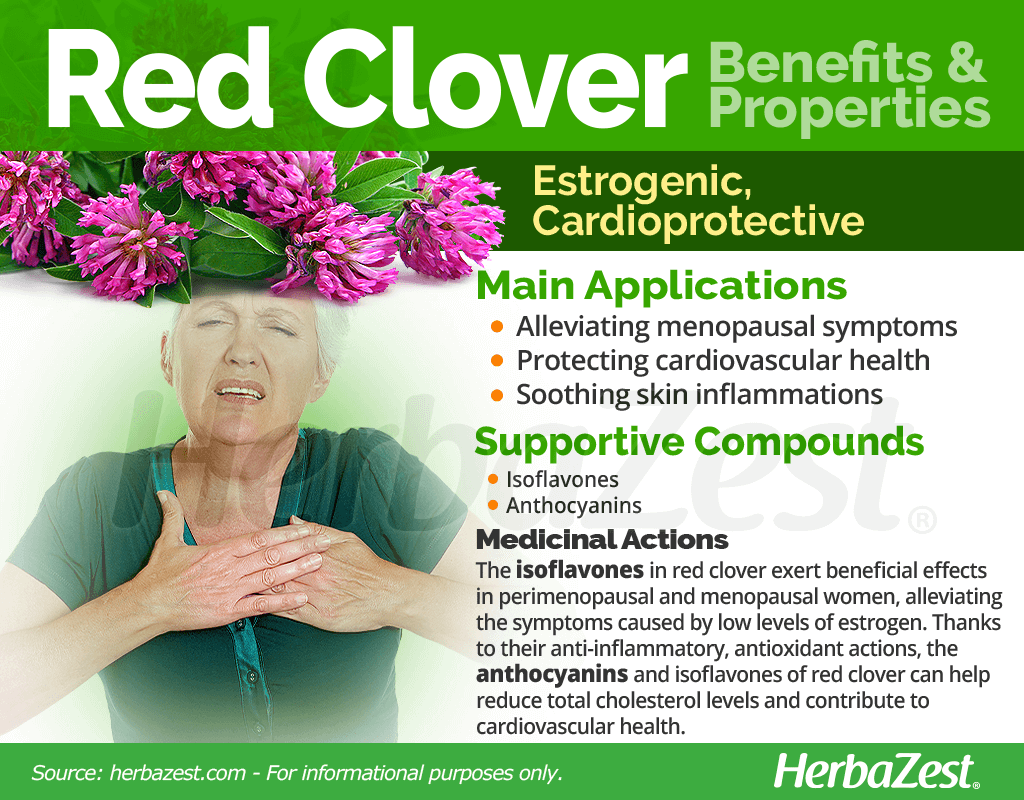
How to Consume Red Clover
The pinkish-red flower of red clover is usually dried and then brewed into a therapeutic infusion. Supplements are also available in the form of liquid extracts, tablets, capsules, and tinctures.
Natural Forms
Infusions. To brew red clover tea, one or two teaspoons of dried flowers are steeped in a glass of water for half an hour.
Powder. The benefits of red clover can be obtained by mixing the powder with beverages and shakes.
Poultice. For common skin problems, such as eczema, psoriasis, and sunburns, the topical application of smashed red clover roots, leaves, stems, and flowers can provide relief from inflammation and pain.
Herbal Remedies and Supplements
Capsules. These supplements typically range from 40 - 160 mg of red clover, which equates to 28 - 85 mg of isoflavones.
Tincture. A tincture of 30% alcohol can be taken as 3 - 5 mL a day alone or added to hot water to be consumed as a tea.
Liquid extract. Like a tincture, a fluid extract can be mixed with hot water. However, the generally-recommended dosage is one milliliter thrice a day.
Essential oil. Red clover essential oil is commonly diluted in water or beverages and used orally for menopausal symptoms – like hot flashes -, mastalgia, and premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
- Ointments. Topical applications of red clover ointment, infusions, or liquid extract can be applied as needed as long as they do not aggravate the skin or touch open wounds.

Growing
Red clover is a short lived perennial, widely cultivated in temperate regions around the world, that grows quickly and prolifically, being relatively adaptable. However, environmental factors that affect red clover yield are soil conditions, temperature, and precipitation during the growing season.
Growing Guidelines
Red clover will do better in loamy soils (as opposed to sandy or gravelly). It prefers well-drained areas, but it is not always necessary for successful growth.
The soil in which red clover is to be grown should be free of weeds. This herb is also more tolerant of shade than other legumes, and, therefore, is commonly grown alongside other grasses.
In the southeastern and western U.S., red clover is typically sown from mid-October to mid-December.
For maximum yields, the soil for red clover requires phosphorus and potash supplementation, although nitrogen will be fixed by the plant itself thanks to rhizobia.
Red clover is infamous for its susceptibility to fungal infections and insect infestations - in particular, to anthracnose species and powdery mildew.
- Life cycle Perennial
- Harvested parts Flowers, Roots, Seeds, Leaves
- Light requirements Full sun, Partial shade
- Soil Medium (loam), Well-drained
- Growing habitat Temperate climates
- Potential diseases Mildew, Anthracnose
Additional Information
Plant Biology
Red clover produces pretty pink, purple, or magenta flowers that are round or oval in shape and 0.5 - 1.0 inch (1.5 - 2.5 cm) in diameter. It can grow to be about 8 - 20 inches (20 - 50 cm) in height on a hairy, upright stem. Its leaves grow in groups of three and have a distinct white or light-green crescent marking.
Classification
As a legume, red clover is part of the Fabaceae family, a large group containing 700 genera and over 17,000 species. Many economically valuable crops belong to this large family, notably including beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), alfalfa (Medicago sativa), chickpeas (Cicer arietinum), fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum), soy (Glycine max), and tamarind (Tamarindus Indica).
Species and Varieties of Red clover
The clover genus, Trifolium, includes about 300 species around the world. Due to its popularity among farmers, there are several red clover varieties to choose from. The newest ones are less susceptible to disease, so they can yield for a few more years from initial planting.
Historical Information
Red clover is native to Europe and the first records of it cultivation date back to approximately 1,000 years ago in Andalucia, Spain, from where its cultivation spread to other countries.
Red clover was among the earliest species introduced into the Americas as a pasture crop, during the 1500's, and appeared in the Northeastern United States in the 18th century.
Nowadays, red clover is widely distributed all over the world where temperate climates are found, including Europe, North America, northern China, Japan, southern Latin America, and southern Australasia.
Economic Data
Red clover was traditionally used as a natural nitrogen fixer crop in Europe; however, with the introduction of synthetic fertilizers after World War II, the size of clover fields started to steadily decrease on a global scale. Currently, emergent medicinal markets for red clover as well as traditional farming practices keep the cultivation of this species alive and thriving.
Currently, red clover represents 41% of the forage grasses cultivated area in Europe, with Italy and the Czech Republic the leading producers, with 19,900 and 11,430 hectares respectively. France comes third with 8,125 hectares.
In North America, the main producers of red clover seed are Canada and the southern area of the United States, whereas Chile is emerging as an important red clover exporter throughout South America.
Other Uses
Fodder. Red clover provides a high value protein content, and it is often used for livestock nutrition.
Fuel. Red clover is also a great source of biomass for biogas production.
Pest control. When grown as cover crop, red clover helps prevent diseases and insect infestations.
Soil remediation. As a perennial species, red clover contributes to environmental protection, helping prevent soil erosion, and it is used in phytoremediation and barren land management.
Fertilizer. Red clover is also prized as being a valuable nitrogen-fixing crop, which is beneficial in the care of a cultivated land.
Silage. It has high nutritional value and constitutes valuable raw material for silage making.
- Other uses Animal feed, Fertilizer, Fuel, Repellent
Sources
- Agriculture Journals, Effect of provenance and ploidity of red clover varieties on productivity,persistence and growth pattern in mixture with grasses, 2010
- Bellarmine University, Red Clover
- Brandeis University, Field Biology Electronic Field Guides | Red Clover
- Cornell University, Medium red clover
- European Seed Certification Agencies Association - ESCAA, Seed production in EU - 2020
- Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry - Alberta - Canada, Red Clover Seed Production
- Oregon State University, Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.)
- Purdue University, Trifolium pratense L.
- Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine, p. 277
- FAOSTAT, Trifolium pratense L.
- New York University - Langone Medical Center, Phytoestrogens
- University of Maryland Medical Center, Red clover
Footnotes:
- Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research. (2012). The effects of red clover on quality of life in post-menopausal women. Retrieved July 7 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3590693/
- Nutrients. (2020). Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Anthocyanins of Trifolium pratense (Red Clover) in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW-267.4 Macrophages. Retrieved July 7 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7230587/
- Photochemistry and Photobiology. (2001). Isoflavonoid compounds from red clover (Trifolium pratense) protect from inflammation and immune suppression induced by UV radiation. Retrieved July 7 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11594062/
- Maturitas. (2020). Effects of red clover (Trifolium pratense) isoflavones on the lipid profile of perimenopausal and postmenopausal women-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Retrieved July 7 from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31883666/