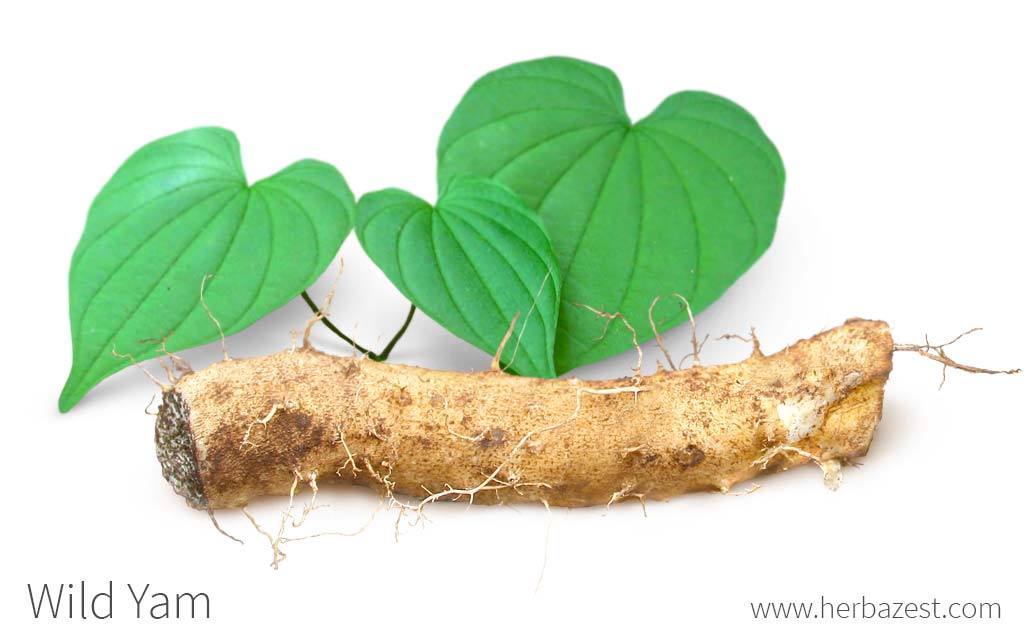
Wild yam has a long history of alimentary and medicinal uses that can be traced back to Native American cultures, before the arrival of the first European settlers. Modern science has revealed the mechanisms behind wild yam's health benefits and expanded its uses to the pharmaceutical industry; however, the folk applications of the herb remain popular among herbalists.
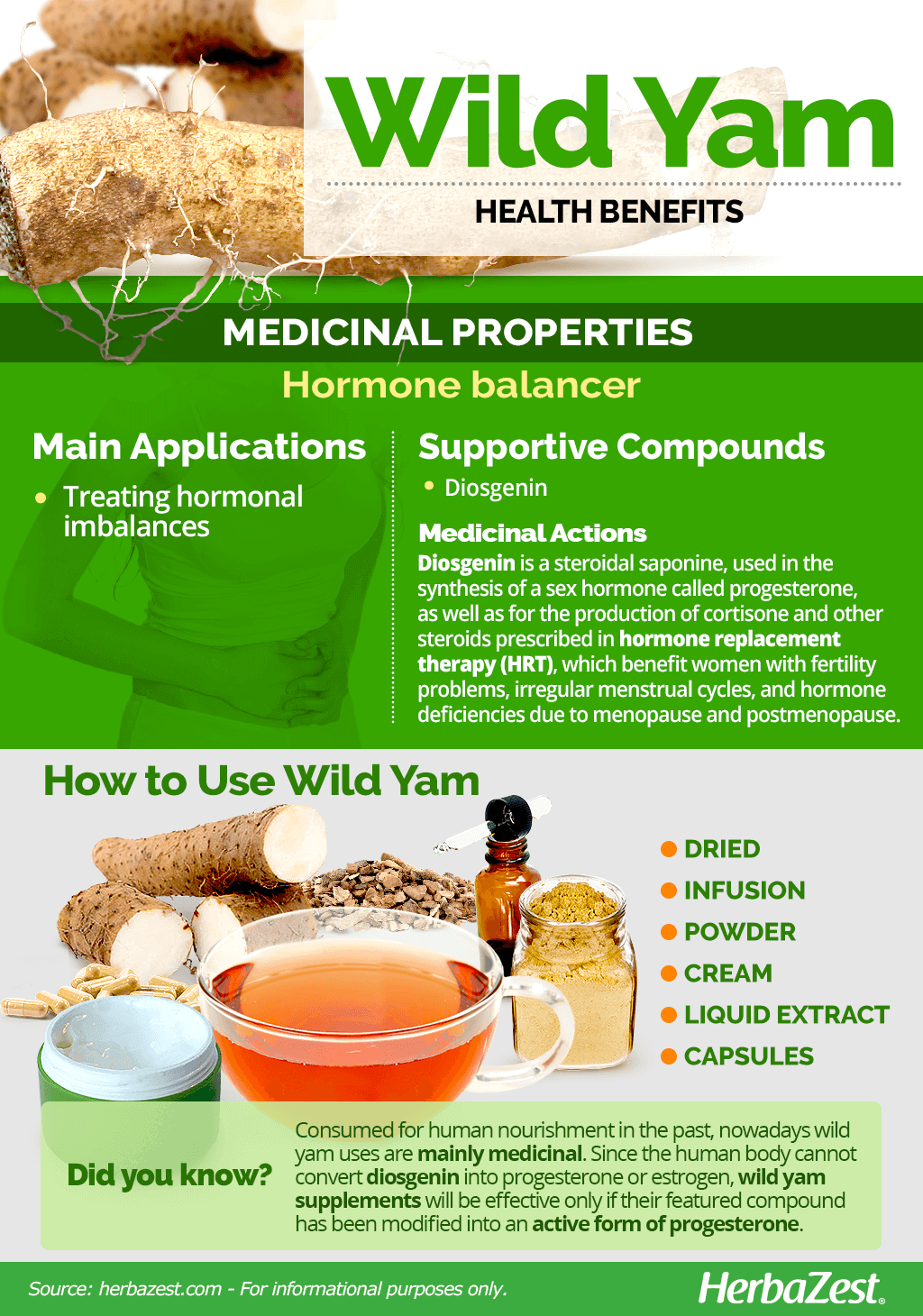
Wild Yam Medicinal Properties
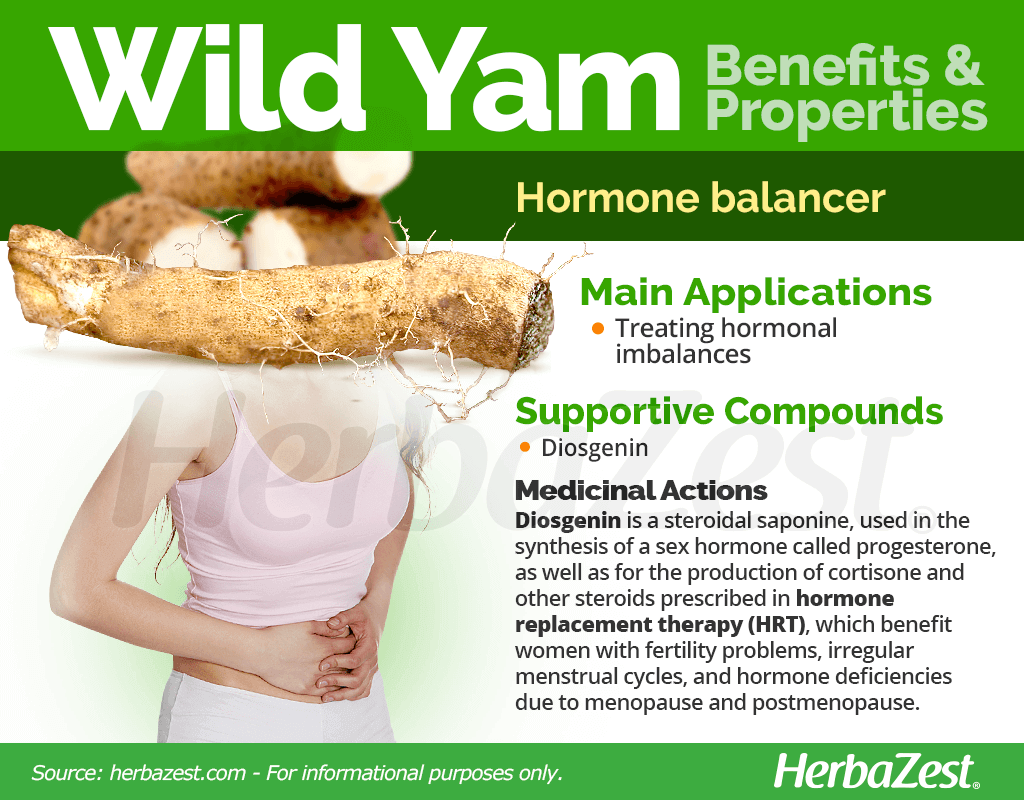
Health Benefits of Wild Yam
Wild yam is a unique herb with a very specific set of properties. Scientific studies have been inclusive about its effectiveness in direct consumption, however the claimed wild yam benefits are yet to be fully corroborated. Nevertheless, wild yam properties have been popularly used for centuries, mainly for the following purpose:
Treating hormonal imbalances. It is thought that wild yam properties help regulate menstrual cycles and support uterine health in menopausal and postmenopausal women.
Additionally, some research suggests that the wild yam root may help eliminate the excess of cholesterol, thus preventing the accumulation of plaque in the arterial walls. It is also thought that wild yam promotes liver health, as well as treating the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
How It Works
Most wild yam benefits have been attributed to steroidal saponins, chiefly diosgenin. However, a number of flavonoids and phytosterols - including sitosterol, stigmasterol, and taraxerol - have also been found in the wild yam root, as well as dioscorine, tannins, starch, vitamin C (ascorbic acid), and beta-carotene.
Wild yam has been found to contain about 3.5% diosgenin, which is primarily used as a source in the synthesis of a sex hormone called progesterone, as well as for the production of cortisone and other steroids prescribed in hormone replacement therapy (HRT),which benefit women with fertility problems, irregular menstrual cycles, and hormone deficiencies due to menopause and post-menopause.
Preliminary studies have also shown the stimulating effects of diosgenin over fat metabolism and bilis production. This compound can inhibit the pancreatic enzymes that aid cholesterol absorption, as well as protecting the liver from oxidative damage.
Diosgenin is widely used as an active compound in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to relieve menopause symptoms and other conditions related to hormonal imbalances.
Herbs like black cohosh and maca root also promote hormonal balance, whereas hypocholesterolemic properties can be found in avocado and walnuts.
Wild Yam Side Effects
The medicinal forms of wild yam are considered relatively safe at established doses and under the supervision of a health specialist. However, large amounts of wild yam taken orally can cause vomiting.
Cautions
Women who are breastfeeding or pregnant, as well as those who have a form of reproductive cancer, endometriosis, or uterine fibroids should not taken wild yam. This herb can interact with medications that contain estrogen, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for menopause symptoms.
- Medicinal action Hormone balancer
- Key constituents Diosgenin
- Ways to use Capsules, Liquid extracts, Ointment
- Medicinal rating (2) Minorly useful plant
- Safety ranking Use with caution
How to Consume Wild Yam
Because of its nutritional content, the wild yam root was once used in culinary dishes; however, due its bitter flavor, this form of consumption has faded in favor of tastier, domesticated yams. Nowadays, wild yam is used mainly as a medicinal herb. It is traditionally consumed in herbal preparations and its active compound, diosgenin, is also available in a variety of over-the-counter products and prescribed drugs for the treatment of hormonal imbalances and menopause.
ALTHOUGH IT WAS USED FOR NOURISHMENT IN THE PAST, NOWADAYS WILD YAM IS USED MOSTLY FOR MEDICINAL PURPOSES.
Natural Forms
Dried. The dried root of wild yam is used to make a variety of medicinal preparations.
Infusion. Wild yam's dried root can be brewed into a medicinal infusion for relieving premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause symptoms.
Powder. In this popular form wild yam benefits can be easily obtained by adding the powdered root to water, smoothies, or green juices.
Herbal Remedies & Supplements
Liquid extract. This herbal preparation provides a higher concentration of diosgenin, allowing for better and faster absorption. In this form, wild yam properties can reduce PMS and menopausal symptoms, as well as protecting liver function.
Cream. The extracts of wild yam can be also absorbed through the skin when applied topically, in the form of a body cream, gently releasing their hormone balancing compounds.
Capsules. This supplemental form of wild yam is taken to stimulate female fertility, as well as for the relief of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause symptoms.
- Edible parts Root
- Taste Bitter

Growing
Wild yam is typically found in either moist open woods, within thickets, or growing along roadsides. It is widely distributed in North America, particularly in the central and southern regions of the United States.
Growing Guidelines
Wild yam seeds should be planted in a partly shaded spot, with well-drained, moist soil.
A pH of 6.0 - 8.0. is ideal for growing wild yam plants.
Seedlings are sensitive to temperature changes, so it is best to grow them in a nursery or in a protected, enclosed area.
Germination can be expected up to three weeks after sowing the seeds.
The top inch (2.5 cm) of soil should be frequently watered, since this plant is highly sensitive to drought.
- Life cycle Perennial
- Harvested parts Roots
- Light requirements Partial shade
- Soil pH 6.1 – 6.5 (Slightly acidic), 6.6 – 7.3 (Neutral), 7.4 – 7.8 (Slightly alkaline)
- Growing habitat Temperate climates
Additional Information
Plant Biology
Wild yam is a perennial vine producing annual stems from a tuberous rootstock. It has heart-shaped leaves, and can grow up to 15 feet (4.5 m) high. The underground stem or rhizome is the most valuable part of the plant. Wild yam produces three-sided fruits, which contain winged seeds that spread by wind.
Classification
Wild yam (Dioscorea villosa) is a member of the Dioscoreaceae family, which contains about 750 species of flowering plants, with commercially produced yams being the best-known species.
Wild yam is also a member of the Dioscorea genus, contains about 600 species spread throughout tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. Yams are this genus's most economically important crop.
Subspecies and Related Species of Wild Yam
No subspecies of wild yam have been identified and no cultivars have been developed to date. Some taxonomists consider wild yam to have one variety, Dioscorea villosa var. hirticaulis. Today, however, this is more widely accepted as a synonym for Dioscorea villosa.
Some relatives of Dioscorea villosa include Mexican wild yam (D. composita or D. mexicana), yam (D. floribunda), and turtle back (D. elephantipes), however North American and Mexican wild yam are the most widely used for medicinal purposes.
Historical Information
The importance of wild yam throughout history dates back to Native American cultures, where it was valued for its nutritional content and medicinal benefits.
By the 18th century, wild yams were introduced to European settlers, who saw it used in local herbal remedies, and occasionally used it as a food crop. In the 1950s, scientific studies were done on the tuber of wild yam, revealing its active compounds and mechanisms of action.
Economic Data
The main economic importance of wild yam lies in its medicinal value, as it has found use as an ingredient in some pharmaceuticals. The United States produces the largest amount of wild yam per year. Although specific statistics on the cultivation and harvesting of wild yam root are unknown, worldwide production of yam species reaches 48.7 million tons per year.
Other Uses
Cosmetic industry. Wild yam can be found as an ingredient in many personal care products, especially body lotions, moisturizers, and butters.
- Other uses Cosmetics
Sources
- Carbohydrate Research, Cholestane steroid glycosides from the root of Dioscorea villosa (wild yam), 2013
- Climateric: the journal of the International Menopause Society, Effects of wild yam extract on menopausal symptoms, lipids and sex hormones in healthy menopausal women, 2001
- Herbs and Natural Supplements, p. 1177
- International Journal of Food Science, Roots and Tuber Crops as Functional Foods: A Review on Phytochemical Constituents and Their Potential Health Benefits, 2016
- International Journal of Toxicology, Final report of the amended safety assessment of Dioscorea Villosa (Wild Yam) root extract, 2004
- National Library of Medicine, Progesterone
- University of Michigan Health, Discorea villosa L.
- Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine, p. 93
- MedlinePlus Herbs and Supplements, Wild yam
- American Cancer Society, Wild Yam
- Medicinal Plants of the World, p. 126
- Germplasm Resources Information, Taxon: Dioscorea villosa L.
- New York University - Langone Medical Center, Wild yam
- University of Maryland Medical Center, Wild yam