It is no news that avocados are exceptionally nutritious. Several studies have shown that the fruit's mono- and polyunsaturated fats as well as phytonutrients offer many benefits for cardiovascular health.1
However, most of these studies focused on exploring the effects of avocados on decreasing heart disease risk factors, such as high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. The purpose of this observational study was to assess the association between long-term avocado consumption and cardiovascular disease.
The Study
Researchers analyzed data pertaining to 110, 487 people (68, 786 women and 41, 701 men) participating in two ongoing long-term studies: the Nurses' Health Study and Health Professionals Follow-Up Study.
They took a look at their dietary intakes (including avocado as well as other fat-containing foods) as well as incident cases of cardiovascular disease over the span of 30 years. The results of this comprehensive study were published in the 2022 edition of the Journal of the American Heart Association.
The Results
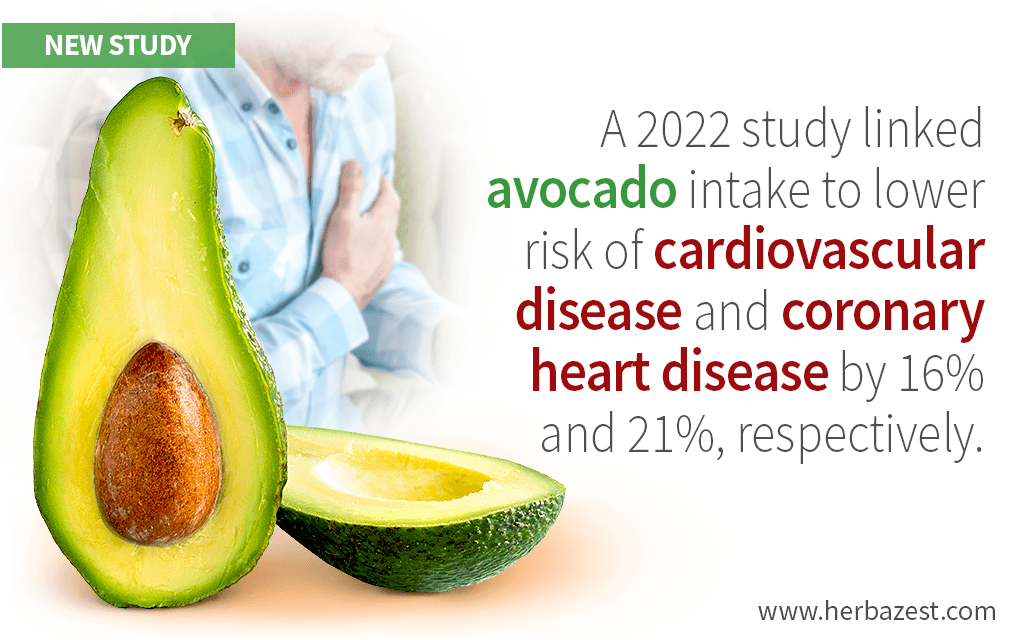
It turned out that participants eating two (or more) avocado servings per week had a 16% lower risk of cardiovascular heart disease, with a 21% lower risk of coronary heart disease in comparison to those who did not eat avocados. No associations were found between avocado consumption and stroke.
Participants with higher avocado intakes also tended to consume a healthier diet, including more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and dairy.
Researchers also found that replacing half a serving per day of margarine, butter, eggs, cheese, yogurt, and processed meats with the same amount of avocado reduced the risk of coronary heart disease by 16% to 22%. For reference, one serving was defined as half an avocado.
What Does this Mean?
The results of this new study indicate that eating avocados lowers the risk of heart disease. Researchers suggest that avocado's role in preventing heart issues lies in its high content of plant-based fats.
These findings are important because they offer easy-to-follow dietary recommendations for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death in the United States.2
Since heart disease can be prevented with a healthy diet and other lifestyle interventions, researchers urge people to consume more plant-based sources of unsaturated fats - like avocado - for heart health promotion.
Other herbs that are rich in heart-friendly fats are sacha inchi, walnuts, and olives.
Sources
- Journal of the American Heart Association, Avocado Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in US Adults, 2022
Footnotes:
- Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. (2013). Hass Avocado Composition and Potential Health Effects. Retrieved March 31, 2022 from https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10408398.2011.556759
- CDC. (2022). Heart Disease Facts. Retrieved March 31, 2022 from https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm