The earliest recorded use of herbs as natural painkillers dates back to Ancient Egypt, 3000 BCE.
Herbs are often overlooked as painkillers in favor of modern Western medicine, such as ibuprofen. In fact, not only do many herbs have anti-inflammatory properties that make them effective natural painkillers, but considerable scientific study has found these five herbs to have pain-relieving effects that are equal - if not superior to - other pharmaceutical medications. Keep reading to learn more.
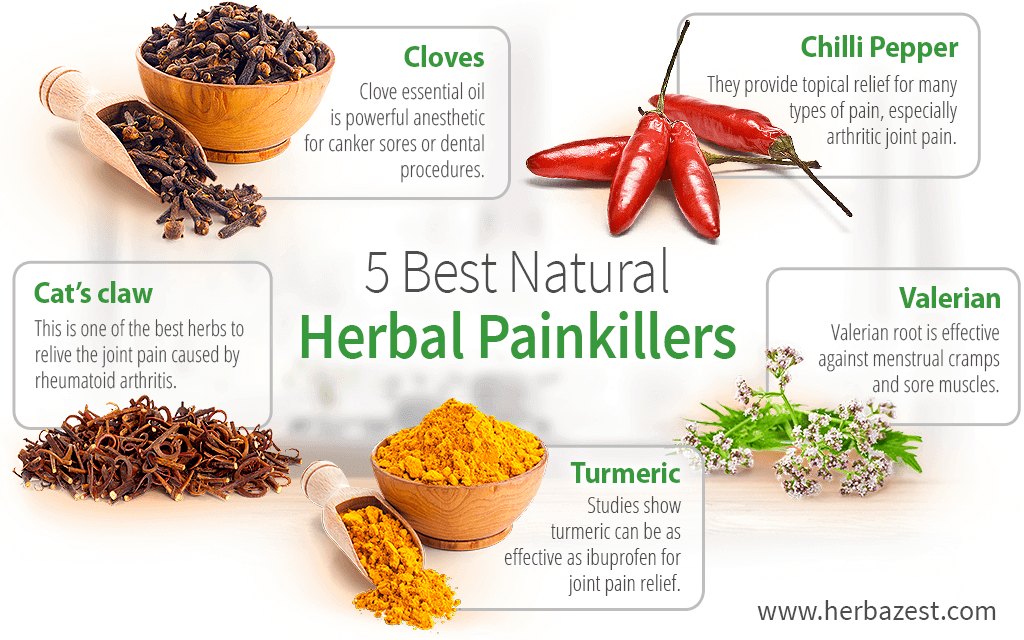
1. Cat's Claw (Uncaria tomentosa)
Cat's claw, also called uña de gato, has anti-inflammatory properties that have been used to alleviate joint pain in conditions such as arthritis. It has also been associated with pain-relief1 alongside harsh cancer and HIV medications, including chemotherapy, radiation treatment, and AZT medication. Cat's claw is available in supplementary form, and can also be applied topically to the point of pain.
2. Chilli Pepper (Capsicum frutescens)
When applied to the skin, capsaicin - the compound that bring the pungency in chilli pepper - causes a temporary sensation of heat and pain, followed by up to several weeks of reversibly desensitized nerve endings with no known lasting effect. The herb has been used to relieve pain caused by shingles, but most successfully in reducing arthritic pain: several studies recorded an 80% pain decrease in the arthritic patients who took part, including those who were already taking medication for the condition2.
3. Cloves (Syzygium aromaticum)
One of the most potent carminatives and a very popular seasoning for desserts, cloves also yield an essential oil with extra medicinal uses3, thanks to its generous eugerol content. When applied topically by the dropful, it makes for an efficient anesthetic, especially for canker sores and dental procedures. However, it is important to keep close control of the dosage, since more than two drops are enough to harm a small child, and even adult dosage shouldn't exceed three drops.
4. Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
The anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric are due to it main active compound, curcumin. A study has discovered it to be equally as effective as ibuprofen for relieving joint pain4; however, because of it slightly spicy nature - commonly used as a curry powder - the best way of consuming turmeric is in supplemental forms, like homemade Turmeric Anti-inflammatory Capsules, though topical application has been found to be effective, too.
5. Valerian (Valeriana officinalis)
Valerian is one of the most powerful existing herbal tranquilizers. It acts as a non-addictive sedative and has been found to relieve muscle and joint pain in an aromatheraputical context (i.e., by adding the herb liberally to bath water)5. Consumption of its root, either as a Valerian Root Anti-Insomnia Tea, or in supplementary form, can soothe pain caused by menstrual cramps and gastrointestinal conditions. Valerian is also helpful against insomnia, so if pain is keeping you awake at night, valerian can promote healthy sleep.
This is just a handful of the known herbs with analgesics properties - the ones that are generally most effective. However, linden, passion flower, California poppy, peony, saffron, and others have been used to this end for centuries. Largely, these herbs are unlikely to interfere with medication you are taking to treat the condition that is causing you pain, but it is best to confirm this with a doctor before you begin to incorporate them into your routine.
Sources
- British Journal of Anaesthesia, Topical capsaicin for pain management: therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of the new high-concentration capsaicin 8% patch, 2011
- National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, Cat's Claw: Science and Safety
- Surgical Neurology International, Natural anti-inflammatory agents for pain relief, 2010
Footnotes:
- Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. (2015). Uncaria tomentosa (cat's claw) improves quality of life in patients with advanced solid tumors. Retrieved August 16, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25495394/
- Clinical therapeutics. (1991). Treatment of arthritis with topical capsaicin: a double-blind trial. Retrieved August 16, 2021, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1954640
- Journal of dentistry. (2012). The effect of clove and benzocaine versus placebo as topical anesthetics. Retrieved August 16, 2021, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16530911
- Journal of alternative and complementary medicine. (2009). Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Retrieved August 16, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19678780/
- International journal of gynaecology and obstetrics. (2011). Effects of valerian on the severity and systemic manifestations of dysmenorrhea. Retrieved August 16, 2021, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21959068/